Carbon Nanotubes History And Production Methods

Overview
History
Synthesis
Purification
Dispersion
Functionalization
Since the discovery of carbon nanotubes (CNTs) in 1991 by Iijima, a whole new discipline in materials science has developed, Nanoscience. Hundreds of millions of dollars have been invested trying to unlock the secrets of these revolutionary materials.
These functional nanoscale materials have a variety of unique, fascinating, and never seen before properties. In fact, a 4th state of matter was recently discovered as water trapped inside a carbon nanotube doesn’t act as a solid, liquid, or gas.
Carbon Nanotubes Overview
Our carbon nanotubes overview is designed to give the reader an in depth understanding of these amazing materials.
On a molecular level, CNTs are 100 times stronger than steel at one-sixth the weight and have a very large aspect ratio making them very useful as a mechanical property enhancing filler material.
Carbon Nanotubes conduct heat and electricity similar to copper but without oxidative concerns provided that they are well dispersed.
Carbon Nanotubes have already found commercial applications in the fields of engineering plastics, polymers, displays, anti corrosion paints, thin films and coatings, transparent and non-transparent conductive electrodes, super hydrophobic coatings and anti-static packaging while active research is on going in fields such as batteries, fuel cells, solar cells, advanced devices, optics, water desalination and many others.
Carbon Nanotubes paved the way for Graphene.

Being a tube-like material. an allotrope of carbon, and having a diameter measuring on the nanometer scale make CNTs a truly revolutionary material. A nanometer is one-billionth of a meter which is about 10,000 times thinner than a human hair.
CNTs are unique due to the strong inter-molecular bonds between the alternating 5 and 6 membered rings of carbon atoms. Van der Waals forces present within carbon nanotubes make them prone to agglomeration/re-agglomeration and achieving good dispersion can be challenging due to those forces as well as their high aspect ratio and high degree of entanglement with other CNTs.
Carbon nanotubes have can have different structures, lengths, thicknesses, and number of layers.
Carbon nanotubes are available as single walled carbon nanotubes, double walled carbon nanotubes, or else as multi walled carbon nanotubes.
The structure of a single walled carbon nanotube can best be visualized as the wrapping of a one-atom-thick layer of graphite called graphene into a seamless, tube-like cylinder even though they are grown as a tube and not as a sheet which is later rolled up.
A structural pattern emerges from the way that the graphene sheet is wrapped which is represented by a pair of indices (n,m). The integers n and m denote the number of unit vectors along two directions in the honeycomb crystal lattice of the carbon nanotubes. If m = 0, the nanotubes are called zigzag nanotubes, and if n = m, the nanotubes are called armchair nanotubes. Otherwise, they are called chiral.
Double walled carbon nanotubes have one concentric nanotube inside another nanotube. Most SWNTs on the market, if made by CCVD contain DWNTs as well.
The electronic characteristics of nanotubes can be different depending on the chiral angle of nanotube as it was grown during synthesis which causes it to act as either semiconducting or metallic material.
They are typically grown as sold as mixed structures. Semiconducting and metallic single walled carbon nanotubes can be successfully isolated by density differentiation.
The process uses chemicals to create a density gradient and the isolated carbon nanotubes gather in specific regions by type which can then be harvested as an isolated material.
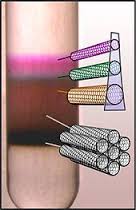
A Carbon Nanotube Density Gradient
The graphene layer that makes up the nanotube can best be envisioned as a rolled-up-chicken-wire-like structure consisting of alternating five and six membered hexagonal rings of carbon atoms.
Their structure is determined by the specific synthesis conditions which rarely produce a homogeneous product as they are usually mixtures of the different types of CNTs produced in a given reaction.
Carbon Nanotubes History
Carbon nanotubes history is perhaps as fascinating as the nanotubes themselves.
In 1980 we knew of only three forms of carbon, namely diamond, graphite, and amorphous carbon. Today we know there is a whole family of other forms of carbon.
The first to be discovered was the hollow, cage-like buckminsterfullerene molecule – also known as the buckyball, or the C60 fullerene.
There are now thirty or more forms of fullerenes, and also an extended family of linear molecules called carbon nanotubes.
C60 is a spherical carbon molecule, with carbon atoms arranged in a soccer ball shape. In the structure there are 60 carbon atoms and a number of five-membered rings isolated by six-membered rings.
The second, slightly elongated, spherical carbon molecule in the same group resembles a rugby ball, has seventy carbon atoms and is known as C70. C70’s structure has extra six-membered carbon rings, but there are also a large number of other potential structures containing the same number of carbon atoms.
Their particular shapes depend on whether five-membered rings are isolated or not, or whether seven-membered rings are present. Many other forms of fullerenes up to and beyond C120 have been characterized, and it is possible to make other fullerene structures with five-membered rings in different positions and sometimes adjoining one another.

A Graphical Representation of a Carbon Fullerene With 60 Carbon Atoms
An important fact for nanotechnology is that useful dopant atoms can be placed inside the hollow fullerene ball or carbon nanotube to tune it’s performance for specific applications.
Atoms contained within the fullerene are said to be endohedral. Of course they can also be bonded to fullerenes outside the ball as salts, if the fullerene can gain electrons.
Possibly more important than fullerenes are carbon nanotubes, which are related to graphite.
The molecular structure of graphite resembles stacked, one-atom-thick sheets of chicken wire – a planar network of interconnected hexagonal rings of carbon atoms.
In conventional graphite, the sheets of carbon are stacked on top of one another, allowing them to easily slide over each other.
That is why graphite is not hard, but it feels greasy, and can be used as a lubricant.
When graphene sheets are rolled into a cylinder and their edges joined, they form CNTs.
Only the tangents of the graphitic planes come into contact with each other, and hence their properties are more like those of a molecule.
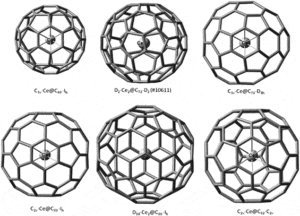
Endohedral fullerenes can be produced in which metal atoms are captured within the fullerene cages.
heory shows that the maximum electrical conductivity is to be expected for endohedral metal atoms, which will transfer three electrons to the fullerene.
Fullerenes can be dispersed on the surface as a monolayer meaning there is only one layer of molecules, and they are said to be mono dispersed.
Provided fullerenes can be placed in very specific locations, they may be aligned to form a fullerene wire. Rice University recently demonstrated Teslaphoresis, using a Tesla coil to self-align carbon nanotubes into a filament.
Systems with appropriate material inside the fullerene ball are conducting and are of particular interest because they can be deposited to produce bead-like conducting circuits.
Combining endohedrally doped structures with non-doped structures changes the actual composition of a fullerene wire, so that it may be tailored in-situ during patterning.
Within a single wire, insulating and conducting regions may be precisely defined. One-dimensional interconnects engineering becomes realistic with fullerenes.

Carbon nanotubes come in a variety of diameters, lengths, and functional group content which can tailor their use for specific applications.
CNTs are available for industrial applications in bulk quantities up metric ton quantities. Several CNT manufacturers have >100 ton per year production capacity for multi walled nanotubes.
A nanotube may consist of one tube of interconnected graphite atoms, a one-atom thick single-wall nanotube, or a number of concentric tubes called multiwalled nanotubes.
When viewed with a transmission electron microscope these tubes appear as planes.
Whereas single walled nanotubes appear as two planes, in multi walled nanotubes more than two planes are observed, and can be seen as a series of parallel lines.
There are different types of CNTs, because the graphitic sheets can be rolled in different ways. How they are rolled is known as the chiral angle.
The three types of CNTs are Zigzag, Armchair, and Chiral. It is possible to recognize zigzag, armchair, and chiral CNTs just by following the pattern across the diameter of the tubes, and analyzing their cross-sectional structure.

Multi walled nanotubes can come in an even more complex array of forms, because each concentric single-walled nanotube can have different structures, and hence there are a variety of sequential arrangements.
The simplest sequence is when concentric layers are identical but different in diameter. However, mixed variants are possible, consisting of two or more types of concentric CNTs arranged in different orders. These can have either regular layering or random layering.
The structure of the nanotube influences its properties – including electrical and thermal conductivity, density, and lattice structure.
Both type and diameter are important. The wider the diameter of the nanotube, the more it behaves like graphite. The narrower the diameter of the nanotube, the more its intrinsic properties depends upon its specific type and is where their properties can be used in new and innovative ways.
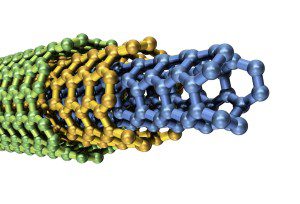
Multi-walled carbon nanotubes (MWNTs) consist of multiple nanotubes inside larger nanotubes with the same and different chiralities.
You can even have semiconducting and metallic regions on the same individual nanotube structure.
Two models best describe the structure of multi-walled carbon nanotubes, the Russian Doll and Parchment models.
Russian Doll model carbon nanotubes are quite literally tubes inside of larger tubes much like the popular children’s toy name would suggest.
Parchment MWNTs features a single sheet of graphite is rolled around itself, resembling a scroll of parchment or a rolled up newspaper.
The interlayer spacing is close to the distance between the individual graphene layers in graphite, approximately 3.4 Å. The Russian Doll structure far much more common.
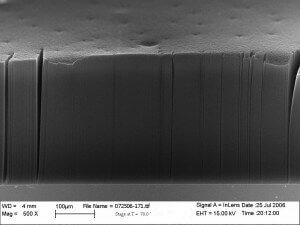
Vertically aligned carbon nanotubes are produced by CCVD and are adhered to the synthesis substrate which is typically Si/SiO2 or stainless steel or copper foils.
They can be grown by CCVD or PECVD in a top down or bottom up synthesis method. The CNTs can be used while on the array or else removed and used free standing.
Some applications such as super capacitors use a roller to flatten the array to make a conductive layer in the device.
Some CNT arrays are drawable meaning they can be directly drawn and spun into fibers.
Carbon Nanotubes Synthesis
There are a number of methods of making CNTs and fullerenes.
Fullerenes were first observed after vaporizing graphite with a short-pulse, high-powered laser, however this was not a practical method for making large quantities. CNTs have probably been around for a lot longer than was first realized.
They were likely made during various carbon combustion and vapor deposition processes, but electron microscopy at that time was not advanced enough to distinguish them from other forms of carbon.
The first method for producing CNTs and fullerenes in reasonable quantities – was by applying an electric current across two carbonaceous electrodes in an inert gas atmosphere.
This method is called plasma arcing. It involves the evaporation of one electrode as cations followed by deposition at the other electrode.
This plasma-based process is analogous to the more familiar electroplating process in a liquid medium. The fullerenes and CNTs are formed by plasma arcing of carbonaceous materials, particularly graphite.
The fullerenes or carbon nanotubes appear in the soot that is formed, while the CNTs are deposited on the opposing electrode.
Another method of nanotube synthesis involves plasma arcing in the presence of cobalt with a 3% or greater concentration.
As noted above, the nanotube product is a compact cathode deposit of rod like morphology. However when cobalt is added as a catalyst, the nature of the product changes to a web, with strands of 1mm or so thickness that stretch from the cathode to the walls of the reaction vessel. The mechanism by which cobalt changes this process is unclear, however one possibility is that such metals affect the local electric fields and hence the formation of the five-membered rings.
Arc Method

The carbon arc discharge method, initially used for producing C60 fullerenes, is the most common and perhaps easiest way to produce CNTs, as it is rather simple.
However, it is a technique that produces a complex mixture of components, and requires further purification to separate the CNTs from the soot and the residual catalytic metals present in the crude product.
This method creates CNTs through arc-vaporization of two carbon rods placed end to end in an enclosure that is usually filled with inert gas at low pressure. The discharge vaporizes the surface of one of the carbon electrodes, and forms a small rod-shaped deposit on the other electrode.
Producing CNTs in high yield depends on the uniformity of the plasma arc, and the temperature of the deposit forming on the carbon electrode.
Hipco method is an arc method synthesis method carried out under high pressure and was developed at Rice University to create high quality single-walled carbon nanotubes (SWCNT) from the gas-phase reaction of iron carbonyl with high-pressure carbon monoxide gas.
Iron pentacarbonyl is used to produce iron nanoparticles that provide a nucleation surface for the transformation of carbon monoxide into carbon during the growth of the nanotubes.
Synthesis produces high quality materials but only in the milligrams range and isn’t commercially scale-able.
Laser Methods
In 1996 CNTs were first synthesized using a dual-pulsed laser and achieved yields of >70wt% purity. Samples were prepared by laser vaporization of graphite rods with a 50:50 catalyst mixture of Cobalt and Nickel at 1200oC in flowing argon, followed by heat treatment in a vacuum at 1000oC to remove the C60 and other fullerenes.
The initial laser vaporization pulse was followed by a second pulse, to vaporize the target more uniformly.
The use of two successive laser pulses minimizes the amount of carbon deposited as soot.
The second laser pulse breaks up the larger particles ablated by the first one, and feeds them into the growing nanotube structure.
The material produced by this method appears as a mat of “ropes”, 10-20nm in diameter and up to 100um or more in length.
Each rope is found to consist primarily of a bundle of single walled nanotubes, aligned along a common axis.
By varying the growth temperature, the catalyst composition, and other process parameters, the average nanotube diameter and size distribution can be varied.
Arc-discharge and laser vaporization are currently the principal methods for obtaining small quantities of high quality CNTs. However, both methods suffer from drawbacks.
The first is that both methods involve evaporating the carbon source, so it has been unclear how to scale up production to the industrial level using these approaches.
The second issue relates to the fact that vaporization methods grow CNTs in highly tangled forms, mixed with unwanted forms of carbon and/or metal species.
The CNTs thus produced are difficult to purify, manipulate, and assemble for building nanotube-device architectures for practical applications.
Catalyzed Chemical Vapor Deposition
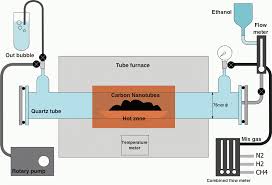
Undoubtedly the most common method of carbon nanotubes synthesis, catalyzed chemical vapor deposition of hydrocarbons over a metal catalyst is a classical method that has been used to produce various carbon materials such as carbon fibers and filaments for over twenty years.
Large amounts of CNTs can be formed by catalytic CVD of acetylene over Cobalt and iron catalysts supported on silica or zeolite.
The carbon deposition activity seems to relate to the cobalt content of the catalyst, whereas the CNTs’ selectivity seems to be a function of the pH in catalyst preparation.
Fullerenes and bundles of single walled nanotubes were also found among the multi walled nanotubes produced on the carbon/zeolite catalyst.
Supported catalysts such as iron, cobalt, and nickel, containing either a single metal or a mixture of metals, seem to induce the growth of isolated single walled nanotubes or single walled nanotubes bundles in the ethylene atmosphere.
The production of single walled nanotubes, as well as double-walled CNTs, on molybdenum and molybdenum-iron alloy catalysts has also been demonstrated.
Methane has also been used as a carbon source. In particular it has been used to obtain ‘nanotube chips’ containing isolated single walled nanotubes at controlled locations.
Ball Milling
Ball milling and subsequent annealing is a simple method for the production of CNTs.
Although it is well established that mechanical attrition of this type can lead to fully nano porous microstructures, it was not until a few years ago that CNTs of carbon and boron nitride were produced from these powders by thermal annealing.
The method consists of placing graphite powder into a stainless steel container along with four hardened steel balls. The container is purged, and argon is introduced. The milling is carried out at room temperature for up to 150 hours.
Following milling, the powder is annealed under an inert gas flow at temperatures of 1400oC for six hours.
The mechanism of this process is not known, but it is thought that the ball milling process forms nanotube nuclei, and the annealing process activates nanotube growth.
Research has shown that this method produces more multi walled nanotubes and few single walled nanotubes.
Other Carbon Nanotube Synthesis Methods
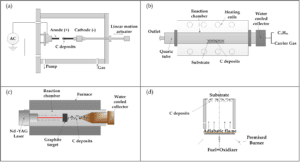
CNTs can also be produced by diffusion flame synthesis, electrolysis, use of solar energy, heat treatment of a polymer, and low-temperature solid pyrolysis.
In flame synthesis, combustion of a portion of the hydrocarbon gas provides the elevated temperature required, with the remaining fuel conveniently serving as the required hydrocarbon reagent.
Hence the flame constitutes an efficient source of both energy and hydrocarbon raw material. Combustion synthesis has been shown to be scalable for high-volume commercial production.
Purification
Purification of CNTs generally refers to the separation of CNTs from other entities, such as carbon nanoparticles, amorphous carbon, residual catalyst, and other unwanted species.
The classic chemical techniques for purification have been tried, but they have not been found to be effective in removing the undesirable impurities.
Three basic methods have been used with varying degrees of success, namely gas-phase, liquid-phase, and intercalation methods and more recently, plasma purification.
Generally, a centrifugal separation is necessary to concentrate the single walled nanotubes in low-yield soot before the micro filtration operation, since the nanoparticles easily contaminate membrane filters.
The advantage of this method is that unwanted nanoparticles and amorphous carbon are removed simultaneously and the CNTs are not chemically modified. However 2-3 mol nitric acid is useful for chemically removing impurities.
A typical purification process is as follows: 1kg CNTs in 20kgs of 20% HNO3 solution at 80-90oC for 6hrs, then it is repeatedly filtered, DI water washed, and filtered until the filtrate solution is PH neutral.
The CNTs are then dried until the form a cake. It is then broken up into a fine powder. Prolonged sonication will damage the CNTs structure due to the harsh acids being used.
It is now possible to cut CNTs into smaller segments, by extended sonication in concentrated acid mixtures.
The resulting CNTs form a colloidal suspension in solvents. They can be deposited on substrates, or further manipulated in solution, and can have many different functional groups attached to the ends and sides of the CNTs.
Gas Phase Carbon Nanotubes Purification
The first successful technique for purification of nanotubes was developed by Thomas Ebbesen and coworkers.
Following the demonstration that nanotubes could be selectively attached by oxidizing gases these workers realized that nanoparticles, with their defect rich structures might be oxidized more readily than the relatively perfect nanotubes.
They found that a significant relative enrichment of nanotubes could be achieved this way, but only at the expense of losing the majority of the original sample.
A new gas-phase method has been developed at the NASA Glenn Research Center to purify gram-scale quantities of single-wall CNTs.
This method, a modification of a gas-phase purification technique previously reported by Smalley and others, uses a combination of high-temperature oxidations and repeated extractions with nitric and hydrochloric acid.
This improved procedure significantly reduces the amount of impurities such as residual catalyst, and non-nanotube forms of carbon) within the CNTs, increasing their stability significantly.
Liquid Phase Carbon Nanotubes Purification Methods
The current liquid-phase purification procedure follows certain essential steps:
- preliminary filtration- to get rid of large graphite particles;
- dissolution- to remove fullerenes (in organic solvents) and catalyst particles (in concentrated acids)
- centrifugal separation-
- microfiltration– and
- chromatography to either separate multi walled nanotubes and unwanted nanoparticles or single walled nanotubes and the amorphous carbon impurities.
It is important to keep the CNTs well-separated in solution, so the CNTs are typically dispersed using a surfactant prior to the last stage of separation.
Intercalation Carbon Nanotubes Purification Methods
An alternative approach to purifying multi walled nanotubes was introduced in 1994 by a Japanese research group.
This technique made use of the fact that nanoparticles and other graphitic contaminants have relatively “open” structures and can therefore be more readily intercalated with a variety of materials that can close nanotubes.
By intercalating with copper chloride, and then reducing this to metallic copper, the research group was able to preferentially oxidize the nanoparticles away, using copper as an oxidation catalyst.
Since 1994, this has become a popular method for purification of nanotubes. Samples of cathodic soot which have been treated this way consist almost entirely of nanotubes.
A disadvantage of this method is that some amount of nanotubes are inevitably lost in the oxidation stage, and the final material may be contaminated with residues of intercalates. A similar purification technique, which involves intercalation with bromine followed by oxidation, has also been described.
Plasma Purification

Plasma purification is a more recent method. In addition to purifying the carbon nanotubes in Argon, the plasma process can be used to covalently bond certain functional groups to the nanotubes surface including OH, COOH, NH2, N2, & F groups.
The plasma process also exfoliates the carbon nanotube material making it more easily dispersed.
Dispersion
To disperse CNTs we recommend the following process using the Sonics VCX 750 or equivalent
We find that sonicating the mixture for 80% of the total time before adding the surfactant solution can enhance the dispersion effect by first well dispersing the carbon nanotubes prior to the surfacant being added to stabilize it.
The reagent polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP) is a good dispersion agent. Some people like to use the reagent Sodium Dodecyl Benzene Sulfonate (SDBS), Triton 100, or Sodium Dodecyl Sulfonate (SDS).
The solution is composed of CNTs, PVP, and water. The required sonication time is 30-60 minutes with an interruption of 30 seconds every 30 seconds to prevent CNT breakage. You must prolong the sonication time accordingly if the power of your ultrasonic equipment is less than that of the SONICS VCX750 unit.
Our sister company CTI Materials LLC has a patented dispersion method which utilizes novel nanoscale materials in lieu of traditional surfactants.
Not only does it not need to be washed numerous times to remove excess surfactants (which can’t be done), it can be reduced to improve conductivity in the end product.
Functionalized Carbon Nanotubes
Pristine nanotubes are hydrophobic and insoluble in many liquids such as water, polymer resins, and most solvents so functionalized carbon nanotubes are often used.
CNTs are difficult to evenly disperse in a liquid matrix such as epoxies and other polymers. This complicates efforts to utilize the nanotubes’ outstanding physical properties in the manufacture of composite materials, as well as in other practical applications which require preparation of uniform mixtures of CNTs with many different organic, inorganic, and polymeric materials.
To make nanotubes more easily dispersible in liquids, it is necessary to physically or chemically attach certain molecules, or functional groups, to their smooth sidewalls without significantly changing the nanotubes’ desirable properties.
This process is called functionalization. The production of robust composite materials requires strong covalent chemical bonding between the filler particles and the polymer matrix, rather than the much weaker van der Waals physical bonds which occur if the CNTs are not properly functionalized.
Functionalization methods such as chopping, oxidation, and “wrapping” of the CNTs in certain polymers can create more active bonding sites on the surface of the nanotubes.
For biological uses, CNTs can be functionalized by attaching biological molecules, such as lipids, proteins, biotins, etc. to them. Then they can usefully mimic certain biological functions, such as protein adsorption, and bind to DNA and drug molecules.
This would enable medially and commercially significant applications such as gene therapy and drug delivery.
In biochemical and chemical applications such as the development of very specific biosensors, molecules such as carboxylic acid (COOH), poly m-aminobenzoic sulfonic acid (PABS), polyimide, and polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) have been used to functionalize CNTs, as have amino acid derivatives, halogens, and compounds. Some types of functionalized CNTs are soluble in water and other highly polar, aqueous solvents.
It is desirable to bond certain chemical functional groups to the carbon nanotube surface to promote dispersion in a specific matrix.
When the CNTs aren’t compatible with the matrix you get “islands of CNTs” meaning your dispersion will have alternating clear portions in an otherwise homogeneous solution.
The main method of functionalization is by re-fluxing in concentrated acids under heat. This does cause some damage to the sidewalls of the CNTs.
This has less of an effect on a multi walled carbon nanotube due as the damage is only on the out walls and the inner walls remain in tact. It can have a dramatic effect on mechanical and conductive properties of single walled nanotubes. Typical chemical functional groups are hydroxyl – OH, Carboxyl – COOH, & Amine – NH2.
A recent method is microwave plasma based functionalization. During plasma based purification, certain process gasses are flowed into the plasma reactor which when excited by the energetic plasma forms covalent bonds between the functional groups and the surface of the carbon nanotubes. Typical functional groups are OH, COOH, NH2, N2, & F groups.
Carbon Nanotubes Properties and Applications
.jpg)
Carbon Nanotubes Properties
- CNTs have high thermal conductivity
- CNTs have high electrical conductivity
- CNTs aspect ratio
- CNTs are very elastic ~18% elongation to failure
- CNTs have very high tensile strength
- CNTs are highly flexible — can be bent considerably without damage
- CNTs have a low thermal expansion coefficient
- CNTs are good electron field emitters
.jpg)
Carbon Nanotubes Applications
- CNTs field emission
- CNTs thermal conductivity
- CNTs energy storage
- CNTs conductive properties
- CNTs conductive adhesive
- CNTs thermal materials
- Molecular electronics based on CNTs
- CNTs structural applications
- CNTs fibers and fabrics
- CNTs biomedical applications
- CNTs Air & Water Filtration
- CNTs catalyst supports
- Other CNT applications
CNTs Electrical Conductivity
There has been significant practical interest in the conductivity of CNTs. CNTs with particular combinations of M and N (structural parameters indicating how much the nanotube is twisted) can be highly conducting, and hence can be considered as metallic. Their conductivity has been proved to be a function of their diameter as well as their chirality (degree of twist). CNTs can be either semi-conducting or metallic in their electrical behavior.
.jpeg)
Conductivity in multi-walled nanotubes (MWNTs) is somewhat intricate. The conductivity of some types of “armchair”-structured CNTs appear to be superior to other metallic CNTs. Moreover, interwall reactions within MWNTs have been found to non-uniformly redistribute the current over individual tubes. However, the current does not change across different parts of metallic single-walled CNTs. However, the behavior of ropes of semi-conducting SWNTs is not similar, as the transport current changes immediately at different positions on the CNTs.
By placing electrodes at different parts of the CNTs, the resistivity and conductivity of ropes of SWNTs have been measured. The resistivity of the SWNT ropes was in the order of 10–4 ohm-cm at 27 °C. This shows that SWNT ropes are the most conductive carbon fibers known. SWNT ropes were able to achieve a current density of 107 A/cm2; however, theoretically, they should be able to sustain much higher stable current densities, as high as 1013 A/cm2.
It has been reported that individual SWNTs may have defects. Unexpectedly, these defects enable the SWNTs to act as transistors. In the same way, combining CNTs together might result in transistor-like devices. A nanotube with a natural junction (where a straight metallic section is joined to a chiral semiconducting section) acts as a rectifying diode, or a half-transistor in a single molecule. In addition, it has recently been reported that SWNTs can direct electrical signals at high speeds (up to 10 GHz) when used as interconnects on semi-conducting devices.
CNTs Strength and Elasticity
The carbon atoms of graphene (a single sheet of graphite) form a planar honeycomb lattice, in which each atom is connected to three neighboring atoms by a strong chemical bond. These strong bonds make the basal-plane elastic modulus of graphite one of the largest among any known material. Therefore, CNTs are expected to be the ultimate high-strength fibers. SWNTs are stiffer compared to steel and are extremely resistant to damage from physical forces. When the tip of a nanotube is pressed, it bends without causing any damage to the tip, and on the removal of the force, the tip returns to its original state. Due to this property, CNTs are very useful as probe tips for very high-resolution scanning probe microscopy.
It has been quite difficult to quantify these effects, and an exact numerical value has not been agreed upon. An atomic force microscope (AFM) can be used to push the unanchored ends of a freestanding nanotube out of their equilibrium position and the force required to push the nanotube can be measured. The current Young’s modulus value of SWNTs is around 1 TPa; however, this value has been uncertain, and a value as high as 1.8 TPa has been reported. Additionally, other values considerably higher than that have been reported. Different experimental measurement techniques might be the reason for the differences. Others have proven theoretically that the Young’s modulus depends on the chirality and size of the SWNTs, ranging from 1.22 to 1.26 TPa. They have calculated a value of 1.09 TPa for a generic nanotube. However, when working with different MWNTs, others have noticed that the modulus measurements of MWNTs using AFM techniques do not have a strong dependence on the diameter. Instead, they argue that the modulus of the MWNTs and the amount of disorder in the nanotube walls are correlated. As expected, when MWNTs break, the outermost layers break first.
CNTs Thermal Conductivity and Expansion
New research from the University of Pennsylvania signifies that CNTs may be the best heat-conducting material ever known to mankind. Ultra-small SWNTs have been shown to exhibit superconductivity even below 20 K. Research suggests that these exotic strands, already heralded for their incomparable strength and unique ability to adopt the electrical properties of either perfect metals or semiconductors, may soon also find applications as miniature heat conduits in a host of materials and devices. Due to the strong in-plane graphitic C-C bonds, they are made remarkably stiff and strong against axial strains. The almost zero in-plane thermal expansion but large inter-plane expansion of SWNTs implies high flexibility and strong in-plane coupling against nonaxial strains. Many applications of CNTs, such as in sensing and actuating devices, nanoscale molecular electronics, or as reinforcing additive fibers in functional composite materials, have been proposed.
Reports of many recent experiments on the preparation and mechanical characterization of CNT-polymer composites have also been presented. These measurements imply modest improvements in strength characteristics of CNT-embedded matrixes in comparison with bare polymer matrixes. Preliminary experiments and simulation studies on the thermal properties of CNTs show very high thermal conductivity. Therefore, nanotube reinforcements in polymeric materials are expected to considerably improve the thermal and thermo-mechanical properties of the composites.
CNTs Field Emission
Field emission is associated with the tunneling of electrons from a metal tip into vacuum, under application of a strong electric field. The high aspect ratio and small diameter of CNTs are very suitable for field emission. A strong electric field is developed at the free end of supported CNTs even for moderate voltages due to their sharpness. De Heer and co-workers observed this at EPFL in 1995. He also immediately realized that these field emitters must be superior to traditional electron sources and might find their way into all kind of applications, most significantly flat-panel displays. It is notable that Samsung actually accomplished a very bright color display only after five years, which will be soon commercialized using this technology.
.jpeg)
During their research on field emission properties of MWNTs, Bonard and co-workers at EPFL observed that light is also emitted along with electrons. This luminescence is induced by the electron field emission because it is not detected when potential is not applied. This light is emitted in the visible part of the spectrum and can sometimes be seen with the naked eye.
.jpeg)
CNTs High Aspect Ratio
CNTs represent a very small, high-aspect-ratio conductive additive for all kinds of plastics. Their high aspect ratio means that a lower loading (concentration) of CNTs is required to realize the same electrical conductivity when compared to other conductive additives. This low loading not only preserves more of the polymer resins’ toughness, especially at low temperatures but also maintains other main performance properties of the matrix resin. CNTs have been established to be an outstanding additive to impart electrical conductivity in plastics. Thanks to their high aspect ratio (about 1000:1), electrical conductivity can be imparted at lower loadings, compared to traditional additive materials such as chopped carbon fiber, stainless steel fiber, or carbon black.
Applications of Carbon Nanotubes
The unique nature of carbon combines with the molecular perfection of single-wall CNTs to endow them with extraordinary material properties, such as very high thermal and electrical conductivity, stiffness, strength, and toughness. It is the only element in the periodic table which bonds to itself in an extended network with the strength of the carbon-carbon bond. The delocalized pi-electron donated by each atom is free to move about the whole structure, instead of remaining with its donor atom, resulting in the first known molecule with metallic-type electrical conductivity. Moreover, an intrinsic thermal conductivity higher than even diamond is offered by the high-frequency carbon-carbon bond vibrations.
.jpeg)
In most materials, however, due to the occurrence of defects in their structure, the actual observed material properties such as strength, electrical conductivity, and so on are degraded very significantly. For example, high-strength steel typically fails at only around 1% of its theoretical breaking strength. However, CNTs achieve values very near to their theoretical limits owing to their molecular perfection of structure. This aspect is part of the unique story of CNTs. CNTs are examples of true nanotechnology: they are only about a nanometer in diameter, but are molecules that can be manipulated physically and chemically in very useful ways. They find an incredible range of applications in electronics, materials science, energy management, chemical processing, and many other fields.
CNTs Thermal Conductivity
CNTs have outstanding heat conductivity, electrical conductivity, and mechanical properties. They are probably the best electron field-emitter possible. They are polymers of pure carbon and can be made to and manipulated using the recognized and extremely rich chemistry of carbon. This offers the opportunity to alter their structure and to optimize their dispersion and solubility. Most notably, CNTs are molecularly perfect, in the sense that they are generally free of property-degrading flaws in the nanotube structure. Their material properties can thus reach close to the very high levels intrinsic to them. Due to these extraordinary characteristics, CNTs can be prospectively used in a number of applications.
CNTs Field Emission Applications
CNTs are the best known field emitters of any material. This is understandable, with regard to their high electrical conductivity, and the unbelievable sharpness of their tip (as the tip’s radius of curvature becomes smaller, the electric field will be more concentrated, resulting in increased field emission; this is the same reason lightning rods are sharp). In addition, the sharpness of the tip also indicates that they emit at specifically low voltage, a key fact for building low-power electrical devices that employ this feature. CNTs can carry an amazingly high current density, probably as high as 1013 A/cm2. Additionally, the current is extremely stable. Field-emission flat-panel displays are an immediate application of this behavior, receiving considerable interest. Unlike conventional cathode ray tube display where a single electron gun is used, CNT-based displays use a separate electron gun (or even many of them) for each individual pixel in the display. Their low turn-on and operating voltages, high current density, and steady, long-lived behavior make CNTs very attractive field emitters in this application. General types of low-voltage cold-cathode lighting sources, electron microscope sources, and lightning arrestors are other applications utilizing the field-emission characteristics of CNTs. [B.Q. Wei, et al, Appl. Phys. Lett. 79 1172 (2001)].
CNTs Conductive Plastics
Over the past five decades, much of the history of plastics has involved their use as a substitute for metals. For structural applications, plastics have progressed tremendously, but not where electrical conductivity is needed, since plastics are very good electrical insulators. This deficiency can be ruled out by loading plastics up with conductive fillers, such as carbon black and larger graphite fibers (the ones used to make golf clubs and tennis rackets). In order to offer the necessary conductivity using conventional fillers, the loading required is typically high, however, leading to heavy parts and, more prominently, plastic parts whose structural properties are highly degraded. It is well known that as the aspect ratio of filler particles becomes high, the loading required to achieve a given level of conductivity becomes low. For this reason, CNTs are perfect because they have the highest aspect ratio of any carbon fiber. Furthermore, their natural tendency to form ropes offers inherently very long conductive pathways even at ultra-low loadings.
This behavior of CNTs is utilized in applications such as electrostatic dissipation (ESD); EMI/RFI shielding composites; coatings for gaskets, enclosures, and other uses; radar-absorbing materials for low-observable (“stealth”) applications; and antistatic materials and (even transparent!) conductive coatings.
CNTs Energy Storage
The intrinsic properties of CNTs make them the preferred material for use as electrodes in capacitors and batteries — two technologies of fast-growing significance. CNTs possess good electrical conductivity, an extremely high surface area (~1000 m2/g), and most importantly, their linear geometry makes their surface very accessible to the electrolyte.
Research has demonstrated that CNTs have the highest reversible capacity of any carbon material for use in lithium-ion batteries [B. Gao, Chem. Phys. Lett. 327, 69 (2000)]. Moreover, CNTs are excellent materials for supercapacitor electrodes [R.Z. Ma, et al., Science in China Series E-Technological Sciences 43 178 (2000)] and are currently being marketed for this application.
In addition, CNTs hold applications in various fuel cell components. They have several properties, such as high thermal conductivity and surface area, making them valuable as electrode catalyst supports in PEM fuel cells. Owing to their high electrical conductivity, they may also be used in gas diffusion layers, besides current collectors. The high strength and toughness-to-weight characteristics of CNTs may also prove useful as part of composite components in fuel cells that are used in transport applications, where durability is paramount.
CNTs Conductive Adhesives and Connectors
The exact properties that make CNTs desirable as conductive fillers for use in ESD materials, electromagnetic shielding, and so on make them suitable for interconnection applications and electronics packaging, including coaxial cables, potting compounds, and adhesives and other types of connectors.
CNTs Molecular Electronics
The idea of building electronic circuits out of the critical building blocks of materials — molecules — has seen growth in the past five years, and is a vital part of nanotechnology. In any electronic circuit, but specifically when dimensions reduce in size to the nanoscale, the interconnections between switches and other active devices become more and more essential. Their ability to be precisely derived, electrical conductivity, and geometry make CNTs the most suitable candidates for the connections in molecular electronics. Furthermore, they have been shown as switches themselves.
CNTs Thermal Materials
The record-setting anisotropic thermal conductivity of CNTs is opening doors to several applications that involve heat transfer. Such an application is found in electronics, specifically advanced computing, where uncooled chips currently regularly exceed 100 °C.
The technology for creating aligned structures and ribbons of CNTs [D.Walters, et al., Chem. Phys. Lett. 338, 14 (2001)] is a step toward achieving extremely efficient heat conduits. Furthermore, composites with CNTs have been demonstrated to significantly increase their bulk thermal conductivity, even at incredibly small loadings.
CNTs Structural Composites
The superior properties of CNTs are not just restricted to thermal and electrical conductivities but also include mechanical properties, such as strength, toughness, and stiffness. These properties pave the way for use in a range of applications exploiting them, including advanced composites that need high values of one or more of these properties.
CNTs Fibers and Fabrics
Recently, fibers spun from pure CNTs have been demonstrated [R.H. Baughman, Science 290, 1310 (2000)] and are experiencing rapid development, together with CNT composite fibers. Such super strong fibers will have several applications such as woven fabrics and textiles, transmission line cables, and body and vehicle armor. CNTs are also being employed in order to make textiles stain resistant.
CNT Catalyst Supports
CNTs intrinsically possess an enormously high surface area; actually, for SWNTs, every atom is not just on one surface — but two surfaces, the interior and exterior of the nanotube. Along with the ability to attach basically any chemical species to their sidewalls (functionalization) offers a prospect for unique catalyst supports. Their electrical conductivity may also be used propitiously in the quest for new catalysts and catalytic behavior.
CNTs Biomedical Applications
Although the exploration of CNTs in biomedical applications is just in progress, it has great potential. Since a great part of the human body is made up of carbon, it is usually considered a very biocompatible material. The growth of cells on CNTs has been demonstrated; therefore, they apparently have no toxic effect. The cells also do not adhere to the CNTs, opening doors for applications such as anti-fouling coatings for ships and coatings for prosthetics.
The ability to functionalize (chemically modify) the sidewalls of CNTs also gives rise to biomedical applications including neuron growth and regeneration, and vascular stents. It has also been demonstrated that a single strand of DNA can be bonded to a nanotube, which can subsequently be effectively inserted into a cell.
CNTs Air and Water Filtration
Several corporations and researchers have already developed CNT-based water and air filtration devices. It has been reported that these filters, apart from blocking the tiniest particles, can also destroy most bacteria. This is one more area where CNTs have already been commercialized and products are available now.
CNTs Ceramic Applications
Materials scientists at UC Davis have produced a ceramic material reinforced with carbon nanotubes. The new material is significantly tougher than traditional ceramics, conducts electricity, and can both conduct heat and function as a thermal barrier, with respect to the nanotube orientation.
Since ceramic materials are very hard and resistant to heat and chemical attack, they are valuable for applications such as coating turbine blades; however, they are also very brittle. The researchers mixed powdered alumina (aluminum oxide) with 5%–10% carbon nanotubes, in addition to 5% finely milled niobium. The mixture was treated with an electrical pulse in a process called spark-plasma sintering by the researchers. This process collates ceramic powders more rapidly and at lower temperatures than traditional processes.
The fracture toughness (resistance to cracking under stress) of the new material is up to five times of that of traditional alumina. The material exhibits electrical conductivity seven times of that of earlier ceramics made with nanotubes. It also has fascinating thermal properties, conducting heat in one direction, along the alignment of the nanotubes and, on the other hand, reflecting heat at right angles to the nanotubes, making it a preferred material for thermal barrier coatings.
Other Carbon Nanotubes Applications
There are several other potential applications for CNTs, including solar collection, nanoporous filters, catalyst supports, and all kinds of coatings. There are almost certainly several surprising applications for this excellent material that will be revealed in the future, and which may prove to be the most significant and valuable ones of all. A number of researchers have been studying the conductive and/or waterproof paper produced using CNTs. CNTs have also been demonstrated to absorb infrared light and may hold applications in the I/R optics industry
Conclusion
We hope that his guide has deepened your understanding of Carbon Nanotubes History And Production Methods and inspired you to integrate carbon nanotubes into your existing processes to enhance certain properties or to develop CNT based applications. We are always happy to discuss applications.


No comments:
Post a Comment